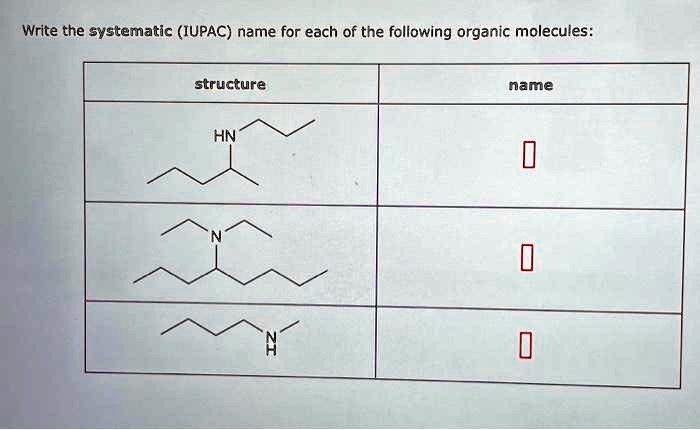
Write the systematic (IUPAC) name for each of the following organic molecules: structure HN name 0 ??? 0 N 0
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
1. First molecule:
Structure shows a secondary amine with:
- A nitrogen atom bonded to:
- A propyl group (three-carbon straight chain)
- A butyl group (four-carbon straight chain)
IUPAC name: N-butylpropan-1-amine
2. Second molecule:
Structure shows a tertiary amine with:
- Nitrogen bonded to:
- A propyl group (three-carbon chain)
- Two ethyl groups (two-carbon chains)
IUPAC name: N-ethyl-N-propylethanamine
3. Third molecule:
Structure shows a primary amine with:
- A straight five-carbon chain with the amine group on the terminal carbon.
IUPAC name: pentan-1-amine
Explanation
In IUPAC nomenclature of amines, the key steps include identifying the longest carbon chain attached to the nitrogen atom and naming the substituents. The simplest classification is by degree: primary amines have one carbon bonded to nitrogen, secondary have two, and tertiary have three.
For compound 1, the nitrogen is bonded to a three-carbon chain (propyl) and a four-carbon chain (butyl). According to IUPAC rules, the longest chain becomes the parent, and the shorter alkyl group is treated as a substituent on the nitrogen. Thus, “N-butylpropan-1-amine” is used, where the “N-” prefix indicates the substituent is on the nitrogen.
Compound 2 has a nitrogen bonded to a propyl and two ethyl groups. The longest chain among these is ethyl (since “ethanamine” is used as the base name). The propyl and one ethyl are treated as substituents on the nitrogen, giving “N-ethyl-N-propylethanamine.”
In compound 3, the structure is a straight chain of five carbon atoms ending with a primary amine group (—NH₂). The parent chain is pentane, and the amine on carbon 1 makes it “pentan-1-amine.”
This naming system avoids ambiguity and reflects the structure of each molecule, helping chemists identify the arrangement of atoms quickly. The use of “N-” in the name clearly shows that the substituent is bonded directly to the nitrogen atom, not the carbon chain.
