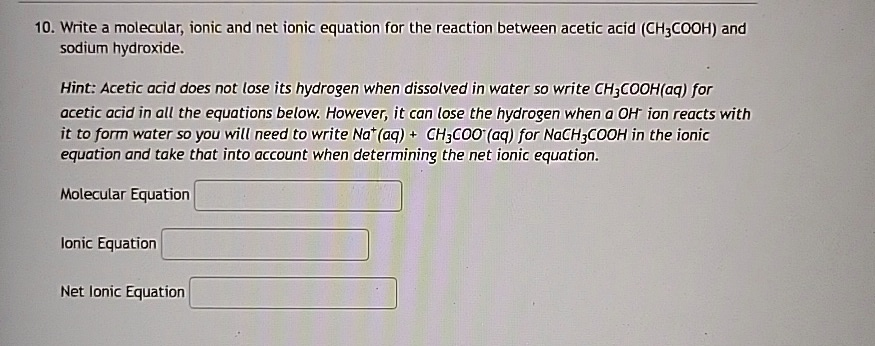
Write a molecular, ionic and net ionic equation for the reaction between acetic acid (CH3COOH) and sodium hydroxide.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
To answer this question, let’s first break down the reaction between acetic acid (CH₃COOH) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
Molecular Equation:
A molecular equation shows the complete compounds involved in a reaction without breaking them down into ions. When acetic acid reacts with sodium hydroxide, it forms sodium acetate and water. The molecular equation is:
CH₃COOH(aq) + NaOH(aq) → CH₃COONa(aq) + H₂O(l)
In this equation, acetic acid (CH₃COOH) reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to form sodium acetate (CH₃COONa) and water (H₂O).
Ionic Equation:
An ionic equation separates all the strong electrolytes (soluble compounds) into their respective ions. Since sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and sodium acetate (CH₃COONa) are both strong electrolytes, they dissociate completely in water. The ionic equation is:
CH₃COOH(aq) + Na⁺(aq) + OH⁻(aq) → Na⁺(aq) + CH₃COO⁻(aq) + H₂O(l)
In this equation, we show sodium ions (Na⁺) and hydroxide ions (OH⁻) dissociating in solution.
Net Ionic Equation:
A net ionic equation removes the spectator ions (ions that appear on both sides of the equation). Spectator ions do not participate in the chemical change. In this case, Na⁺ is a spectator ion because it appears on both sides of the ionic equation. The net ionic equation is:
CH₃COOH(aq) + OH⁻(aq) → CH₃COO⁻(aq) + H₂O(l)
This is the simplified version of the ionic equation where only the species directly involved in the chemical reaction are shown.
Explanation:
- Acetic acid (CH₃COOH) donates a hydrogen ion (H⁺) to the hydroxide ion (OH⁻) from sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
- This forms water (H₂O) and the acetate ion (CH₃COO⁻).
- The sodium ion (Na⁺) is a spectator ion and does not participate directly in the reaction, so it is omitted in the net ionic equation.
