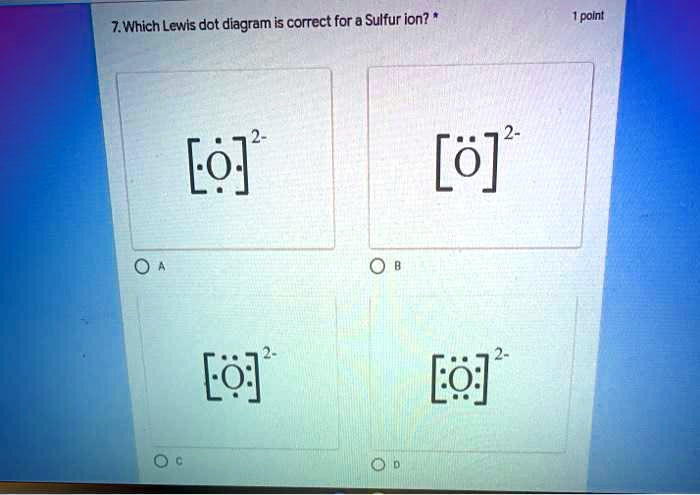
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
The correct answer is Option C.
Explanation: Sulfur (S) is an element in Group 16 of the periodic table. This group, known as the chalcogens, contains elements with six valence electrons in their neutral state. To attain a stable electronic configuration similar to that of a noble gas, sulfur tends to gain two additional electrons, forming a sulfide ion with a charge of 2⁻.
A Lewis dot diagram is a visual representation of the valence electrons surrounding an atom or ion. For a neutral sulfur atom, we would expect six dots around the atomic symbol, each representing a valence electron. However, when sulfur becomes a sulfide ion, it gains two more electrons, bringing the total to eight. This configuration satisfies the octet rule, which states that atoms are most stable when they possess eight electrons in their outermost shell.
In the diagrams provided, Option C depicts sulfur with eight electrons shown as dots around the symbol “S,” enclosed in square brackets with a superscript 2⁻ charge outside. This accurately reflects both the electron gain and the resulting negative charge of the ion. The brackets indicate that the electrons are associated with an ion rather than a neutral atom, and the charge shows the net gain of two electrons.
Option A and Option B each show sulfur with only six valence electrons, which would correspond to a neutral atom. Option D, although similar to Option C, may differ in formatting or clarity depending on the specific expectations of the assignment or test format.
Understanding Lewis diagrams is essential for explaining chemical bonding. They help visualize how atoms interact through the gain, loss, or sharing of electrons. In ionic bonding, as in the case of sulfur forming a sulfide ion, the correct depiction of valence electrons is crucial for predicting compound formation and chemical reactivity.
