The unified atomic mass unit is defined to be 1 u = 1.6605×10−27 kg.
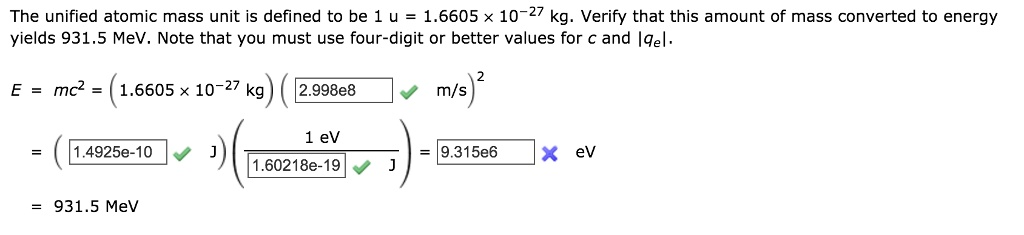
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Based on the provided calculation, the correct value for the final blank box is 9.315e8.
Explanation
The problem requires verifying the energy equivalence of one unified atomic mass unit (u), which is stated to be 931.5 Mega-electron-volts (MeV). This verification process is based on Albert Einstein’s famous⁻¹⁹ J/eV)
Energy (eV) ≈ 931,500,000 eV, which is written in scientific notation as 9.315 x 10⁸ eV.
This value, 9.315 x 10⁸ eV, is the correct entry for the box that was marked as incorrect in the image.
The final step is to convert the energy from electron-volts to mega-electron-volts. The prefix “mega” means one million, so 1 MeV = 10⁶ eV. We divide the energy in eV by 10⁶:
Energy (MeV) = (9.315 x 10⁸ eV) / (10⁶ eV/MeV) = 931.5 MeV.
This calculation successfully verifies that 1 u of mass is equivalent to 931.5 MeV of energy. mass-energy equivalence principle, described by the equation E = mc².
Step 1: Calculate the Energy in Joules
The first step is to calculate the energy (E) in the standard SI unit, Joules (J). We use the given mass m = 1.6605 x 10⁻²⁷ kg for 1 u. The problem specifies using a value for the speed of light (c) with at least four-digit precision. The calculation in the image uses c = 2.998 x 10⁸ m/s.
Plugging these values into the formula:
E = (1.6605 x 10⁻²⁷ kg) * (2.998 x 10⁸ m/s)²
E ≈ 1.4925 x 10⁻¹⁰ J
This result matches the first calculated value in the image, confirming the initial step is correct.
Step 2: Convert Joules to Electron-Volts (eV)
For energies at the atomic and subatomic levels, the Joule is an inconveniently large unit. A more common unit is the electron-volt (eV). The conversion factor between Joules and electron-volts is the elementary charge, |q_e|. The problem uses a high-precision value for this conversion: 1 eV = 1.60218 x 10⁻¹⁹ J.
To convert the energy from Joules to electron-volts, we divide the energy in Joules by this conversion factor:
E (in eV) = (1.4925 x 10⁻¹⁰ J) / (1.60218 x 10⁻¹⁹ J/eV)
E ≈ 931,550,000 eV or 9.3155 x 10⁸ eV
This result, 9.3155 x 10⁸, is the correct value for the final blank box. The image shows that an incorrect value of 9.315e6 was entered, which is off by a factor of 100. The correct exponent is 8.
Step 3: Convert Electron-Volts to Mega-electron-volts (MeV)
The final step is to express this energy in Mega-electron-volts. The prefix “Mega” (M) represents a factor of one million, or 10⁶. To convert from eV to MeV, we divide by 10⁶:
E (in MeV) = (9.3155 x 10⁸ eV) / (10⁶ eV/MeV)
E ≈ 931.55 MeV
Rounding this to one decimal place gives 931.5 MeV, which successfully verifies the initial statement.
