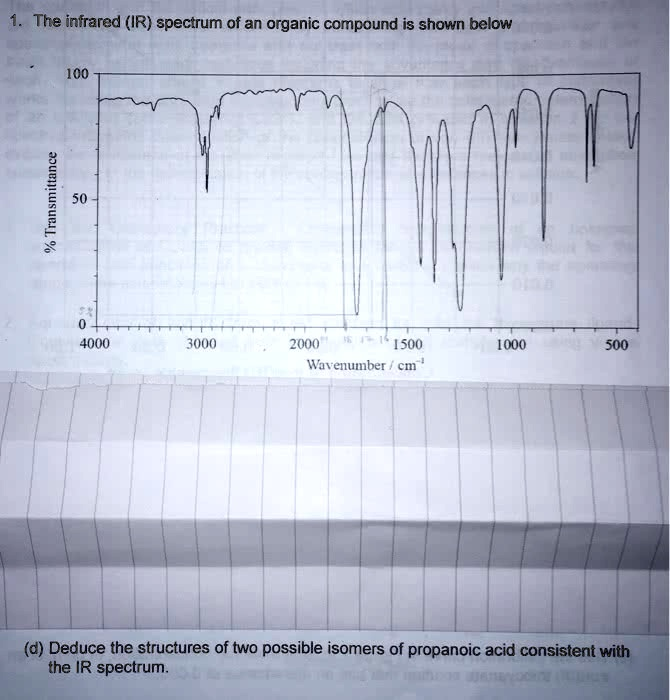
The infrared (IR) spectrum of an organic compound is shown below % Transmittance 100 50 0 4000 3000 2000 1500 1000 500 Wavenumber / cm
(d) Deduce the structures of two possible isomers of propanoic acid consistent with the IR spectrum.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
To answer part (d) — deducing two possible isomers of propanoic acid consistent with the IR spectrum — we must first analyze the spectrum provided and identify the key absorption peaks that indicate functional groups present.
Key IR Peaks and Interpretation:
- Broad absorption around 2500–3300 cm⁻¹:
- This is characteristic of the O–H stretch of a carboxylic acid. The broad and irregular shape supports this interpretation.
- Sharp peak near 1710 cm⁻¹:
- This corresponds to the C=O stretching vibration typical of carboxylic acids.
- Multiple peaks in the fingerprint region (below 1500 cm⁻¹):
- These are consistent with various C–H bending vibrations and other molecular features. While not individually diagnostic, they help confirm the molecular structure.
Conclusion:
The compound is a carboxylic acid, consistent with propanoic acid (CH₃CH₂COOH). Isomers of propanoic acid are compounds with the same molecular formula (C₃H₆O₂) but different structures.
Two Possible Isomers Consistent with the IR Spectrum:
- Propanoic acid (CH₃CH₂COOH):
- A straight-chain carboxylic acid.
- Shows both O–H and C=O stretches.
- No branching or other functional groups.
- 2-hydroxypropanal (CH₃CH(OH)CHO):
- While technically not a positional isomer of a carboxylic acid, it is a constitutional isomer with the same molecular formula.
- Contains an aldehyde (C=O around 1720 cm⁻¹) and hydroxyl (O–H around 3300 cm⁻¹).
- However, this structure may not match as well due to the absence of a broad, strong carboxylic O–H stretch.
A better second candidate:
Methyl formate (HCOOCH₃):
- An ester, another isomer of C₃H₆O₂.
- Esters show a C=O stretch around 1740 cm⁻¹ and a C–O stretch near 1200 cm⁻¹.
- However, the broad O–H peak is absent in esters, so it’s less likely given the spectrum.
Final answer:
- Propanoic acid (CH₃CH₂COOH)
- 2-hydroxypropanoic acid (lactic acid, CH₃CH(OH)COOH) — a plausible isomer with similar O–H and C=O signals, consistent with the IR spectrum.
