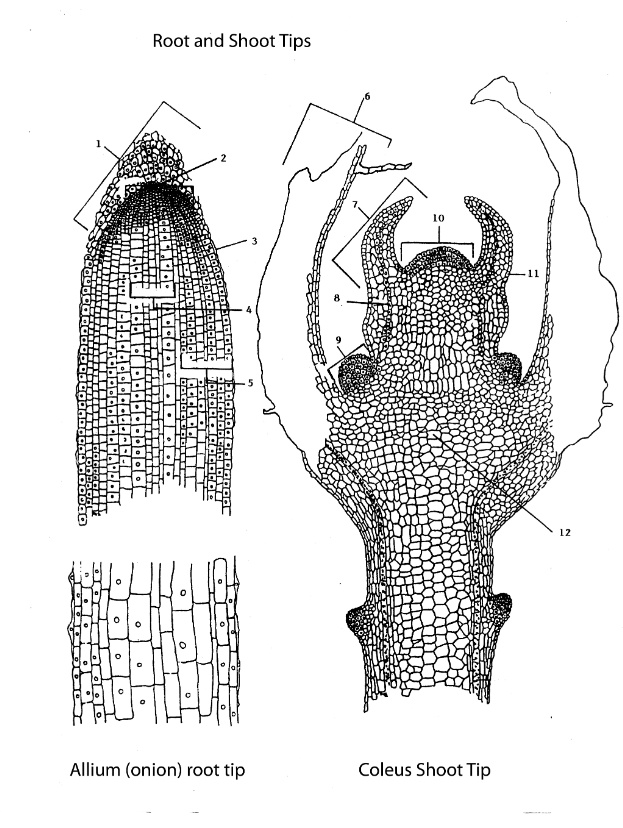
Root and Shoot Tips 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Allium (onion) root tip Coleus Shoot Tip
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Here is the correct identification of the structures labeled on the diagrams:
Allium (onion) root tip
- Root cap
- Apical meristem
- Region of elongation
- Region of maturation
- Vascular cylinder
Coleus shoot tip
- Leaf primordium
- Apical meristem
- Axillary bud primordium
- Ground meristem
- Protoderm
- Procambium
- Vascular tissue
The Allium root tip and the Coleus shoot tip are classic examples used to illustrate primary plant growth. In the Allium root tip, the root cap (1) protects the delicate dividing cells of the apical meristem (2) as the root pushes through the soil. Directly above the apical meristem is the region of elongation (3), where cells rapidly expand to increase the root’s length. Following this is the region of maturation (4), where cells differentiate into specialized types such as xylem and phloem. At the center lies the vascular cylinder (5), which facilitates the transport of water, nutrients, and food.
In the Coleus shoot tip, the leaf primordia (6) are early structures that will develop into leaves. The apical meristem (7) contains undifferentiated cells that fuel growth of the shoot. Just below this are the axillary bud primordia (8), which may later develop into side branches. The ground meristem (9) gives rise to the ground tissues including cortex and pith. The protoderm (10) forms the outermost layer that will become the epidermis. The procambium (11) is the precursor to vascular tissues, and the vascular tissue (12) is already partially differentiated.
These regions highlight how meristematic activity and cellular differentiation contribute to vertical growth in roots and shoots. Understanding these zones is crucial in developmental botany and plant physiology.
