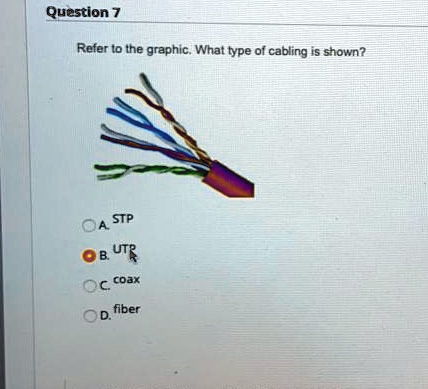
Refer to the graphic. What type of cabling is shown? A. STP B. UTP C. coax D. fiber
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
The correct answer is B. UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair).
Unshielded Twisted Pair is a common type of copper cabling made up of pairs of insulated wires twisted together. These twists are not simply cosmetic—they play a functional role in reducing electromagnetic interference and crosstalk from neighboring cables. UTP cabling is widely used in Ethernet networks and telephone systems because of its low cost, ease of installation, and versatility.
UTP cables typically come in categories based on performance, such as Cat5e, Cat6, or Cat6a. Each category determines maximum transmission speed, bandwidth, and distance limitations. For example, Cat5e can support data rates up to 1 Gbps, while Cat6 and Cat6a offer up to 10 Gbps with improved shielding between internal pairs.
In contrast to STP (Shielded Twisted Pair), UTP lacks an overall shielding foil or braid around the twisted pairs. This means UTP is more susceptible to interference in electrically noisy environments. However, its reduced bulk and flexibility make it easier to install, particularly in spaces where minimal electrical interference exists.
Coaxial cables use a single copper conductor and are covered by layers of insulation and shielding, mainly serving applications like television transmission and broadband internet. Fiber optic cables are completely different in construction. They transmit data as light signals through glass or plastic fibers, offering extremely high bandwidth and immunity to electrical interference but at higher costs and complexity.
The cable shown in the image clearly presents multiple colored wire pairs twisted around each other without any metallic shielding, which visually identifies it as UTP. Understanding these physical characteristics can help in correctly identifying cable types and selecting the right solution for specific networking needs.
