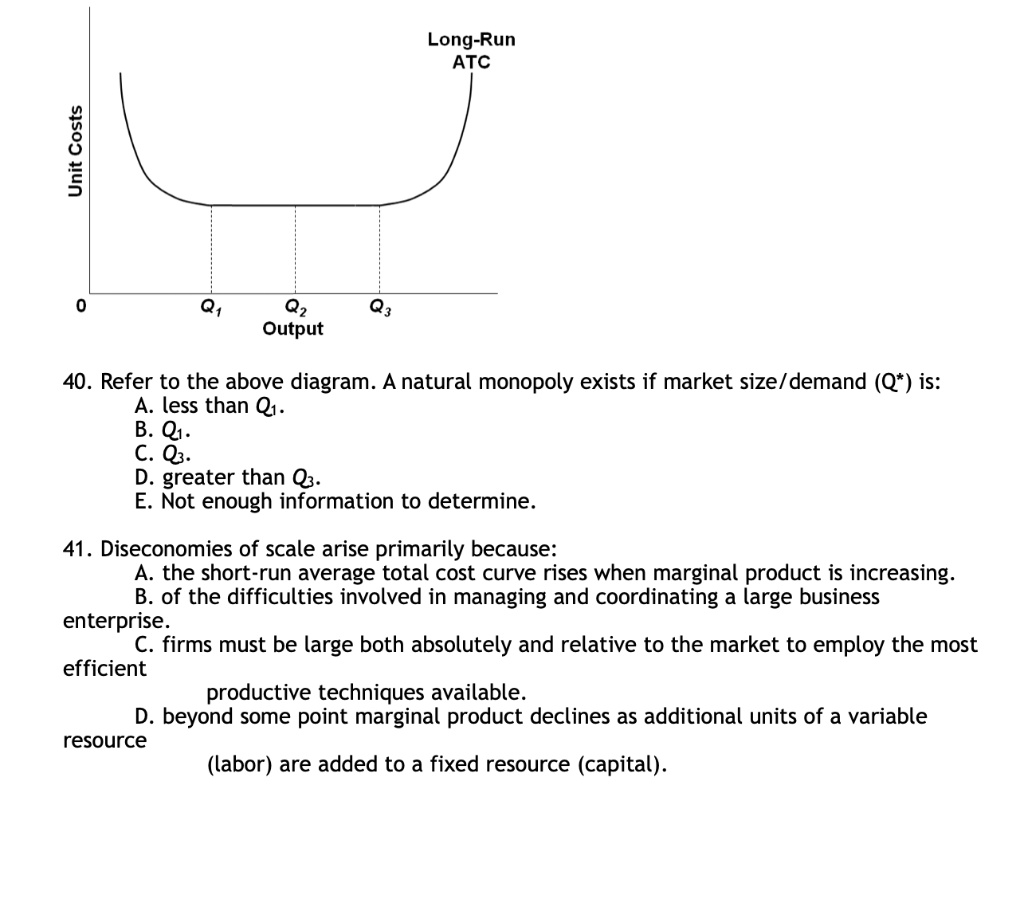
Unit Costs 0 Q1 Q2 Output Q3 Long-Run ATC 40. Refer to the above diagram. A natural monopoly exists if market size/demand (Q*) is: A. less than Q1. B. Q1. C. Q3. D. greater than Q3. E. Not enough information to determine. 41. Diseconomies of scale arise primarily because: A. the short-run average total cost curve rises when marginal product is increasing. B. of the difficulties involved in managing and coordinating a large business enterprise. C. firms must be large both absolutely and relative to the market to employ the most efficient productive techniques available. D. beyond some point marginal product declines as additional units of a variable resource (labor) are added to a fixed resource (capital).
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
To answer the questions from the diagram and accompanying details:
40. A natural monopoly exists if market size/demand (Q*) is:
- A natural monopoly occurs when a firm can produce the entire market supply at a lower cost than if there were multiple firms in the industry. This typically happens when the firm experiences economies of scale over a large range of output, meaning the cost per unit decreases as production increases.
In the graph, we see that the long-run average total cost (ATC) curve is continuously decreasing over the output range from 0 to Q1, and at Q1, the ATC curve is still decreasing. The firm can serve the entire market at a lower cost than if there were multiple firms. Therefore, a natural monopoly exists if the market size (Q*) is at or less than Q1 because beyond Q1, the firm would have to deal with diseconomies of scale.
- The correct answer is A. less than Q1.
41. Diseconomies of scale arise primarily because:
- Diseconomies of scale refer to the situation where a firm’s cost per unit increases as it increases output. This typically happens when the firm becomes too large, and inefficiencies arise due to factors like management difficulties, reduced worker productivity, or difficulty in coordinating operations.
- The best explanation for diseconomies of scale comes from the fact that after a certain point, adding more units of a variable resource, such as labor, to a fixed resource, such as capital, causes marginal product (the additional output per unit of input) to decline. This reduces the efficiency of production.
- The correct answer is D. beyond some point marginal product declines as additional units of a variable resource (labor) are added to a fixed resource (capital).
This explanation describes the primary cause of diseconomies of scale, where firms experience inefficiency when they grow beyond their optimal size.
