Predict the product of the following reaction sequence. i. NaOC
H
ii. CH
CH
CH
Br iii. NaOH iv. H
O
, heat OH OH 0 IV A) I B) II ? II III OH V C) III 6) D) IV E) V 7) 7) What is the product, L, of the following reaction sequence? i. EtBr EtO
C-CO
Et + NaOEt ii. (CH
)
COK iii. Mel iv. NaOH, heat ? v. H
O
, heat (-CO
) 0 00 Me 0 Et Me MeO OEt EtO
C CO
Et Et EtO
C CO
Et ? ? ? I II III 0000 OH HO ? OH 0 Me Et IV V A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V
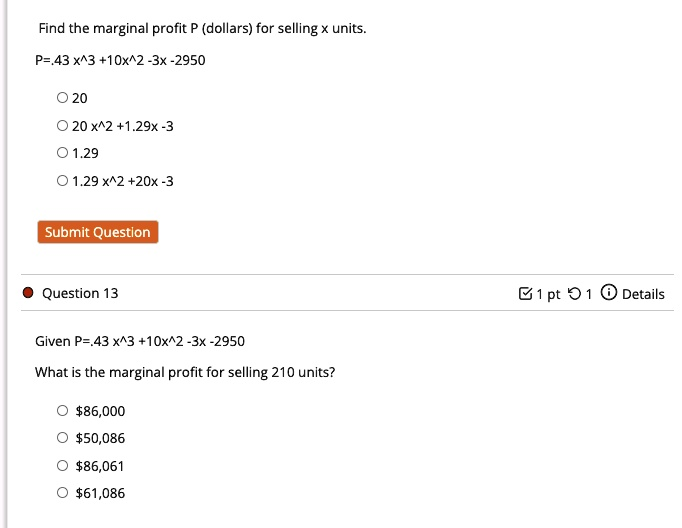
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Here are the solutions to the problems presented in the image.
Correct Answers:
- For the first problem, “Find the marginal profit P (dollars) for selling x units,” the correct answer is 1.29 x^2 + 20x – 3.
- For the second problem (Question 13), “What is the marginal profit for selling 210 units?”, the correct answer is $61,086.
Detailed Explanation
The problems involve finding and evaluating a marginal profit function, which is a fundamental application of differential calculus in economics and business.
Part 1: Finding the Marginal Profit Function
The concept of marginal profit refers to the change in total profit resulting from producing and selling one additional unit. Mathematically, the marginal profit is the first derivative of the total profit function.
The given profit function is:
P(x) = 0.43x³ + 10x² – 3x – 2950
To find the marginal profit function, which we can denote as P'(x), we must differentiate P(x) with respect to x. We will use the power rule of differentiation, which states that for a term axⁿ, its derivative is n⋅axⁿ⁻¹.
Let’s differentiate the profit function term by term:
- Differentiate 0.43x³: Applying the power rule, the derivative is (3) * (0.43) * x⁽³⁻¹⁾ = 1.29x².
- Differentiate 10x²: The derivative is (2) * (10) * x⁽²⁻¹⁾ = 20x¹ = 20x.
- Differentiate -3x: This term can be written as -3x¹. Its derivative is (1) * (-3) * x⁽¹⁻¹⁾ = -3x⁰. Since any non-zero number raised to the power of 0 is 1, this simplifies to -3.
- Differentiate -2950: This is a constant term. The derivative of any constant is 0.
Combining these derivatives gives us the marginal profit function:
P'(x) = 1.29x² + 20x – 3 + 0
P'(x) = 1.29x² + 20x – 3
This matches the fourth option provided in the first question.
Part 2: Calculating the Marginal Profit for 210 Units
Question 13 asks for the specific value of the marginal profit when 210 units are sold. This requires us to evaluate the marginal profit function, P'(x), at x = 210.
Using the function we derived in Part 1:
P'(x) = 1.29x² + 20x – 3
Now, substitute x = 210 into this equation:
P'(210) = 1.29(210)² + 20(210) – 3
Let’s perform the calculation step by step:
- First, calculate (210)²: 210 * 210 = 44,100.
- Next, multiply this by 1.29: 1.29 * 44,100 = 56,889.
- Then, calculate the middle term: 20 * 210 = 4,200.
- Finally, assemble the equation with these values:
P'(210) = 56,889 + 4,200 – 3
Adding the first two numbers:
56,889 + 4,200 = 61,089
Subtracting the last number:
61,089 – 3 = 61,086
The marginal profit for selling 210 units is $61,086. This figure represents the estimated profit the company would gain from selling the 211th unit. This corresponds to the fourth option for Question 13.
