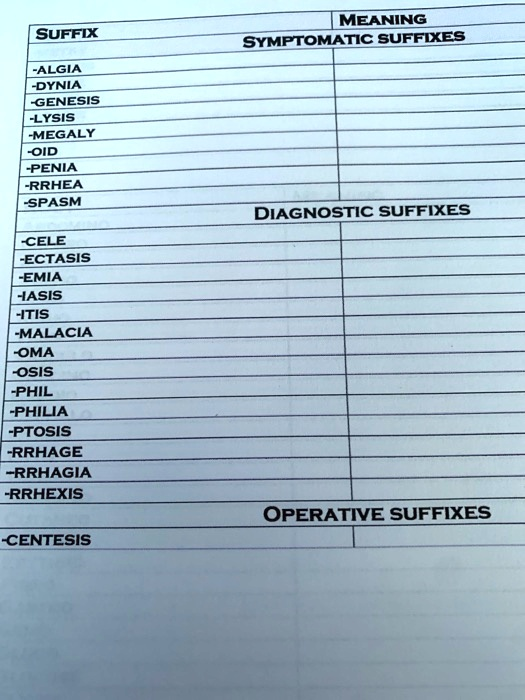
MEANING SUFFIX SYMPTOMATIC SUFFIXES -ALGIA -DYNIA -GENESIS -LYSIS -MEGALY -OID -PENIA -RRHEA -SPASM DIAGNOSTIC SUFFIXES -CELE -ECTASIS -EMIA -IASIS -ITIS -MALACIA -OMA -OSIS -PHIL -PHILIA -PTOSIS -RRHAGE -RRHAGIA -RRHEXIS OPERATIVE SUFFIXES -CENTESIS
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Here is the correct meaning of the suffixes categorized into Symptomatic, Diagnostic, and Operative suffixes:
Symptomatic Suffixes
These suffixes describe signs, symptoms, or conditions that a patient experiences:
- -algia: pain (e.g., neuralgia — nerve pain)
- -dynia: pain (e.g., gastrodynia — stomach pain)
- -genesis: formation or origin (e.g., pathogenesis — origin of a disease)
- -lysis: breakdown, destruction, or loosening (e.g., hemolysis — destruction of red blood cells)
- -megaly: enlargement (e.g., hepatomegaly — liver enlargement)
- -oid: resembling (e.g., lipoid — fat-like)
- -penia: deficiency or lack (e.g., leukopenia — low white blood cell count)
- -rrhea: flow or discharge (e.g., diarrhea — excessive discharge from bowels)
- -spasm: involuntary contraction (e.g., bronchospasm — sudden contraction of the airways)
Diagnostic Suffixes
These suffixes relate to conditions or diagnoses:
- -cele: hernia or swelling (e.g., meningocele — hernia of meninges)
- -ectasis: dilation or expansion (e.g., bronchiectasis — dilation of bronchi)
- -emia: blood condition (e.g., anemia — lack of red blood cells)
- -iasis: abnormal condition or presence of (e.g., cholelithiasis — presence of gallstones)
- -itis: inflammation (e.g., arthritis — inflammation of joints)
- -malacia: softening (e.g., osteomalacia — softening of bones)
- -oma: tumor or mass (e.g., carcinoma — cancerous tumor)
- -osis: abnormal condition (e.g., fibrosis — abnormal formation of fibrous tissue)
- -phil / -philia: attraction or affinity for (e.g., hemophilia — love for blood/clotting disorder)
- -ptosis: drooping or prolapse (e.g., nephroptosis — drooping kidney)
- -rrhage / -rrhagia: bursting forth, excessive flow (e.g., hemorrhage — profuse bleeding)
- -rrhexis: rupture (e.g., cardiorrhexis — rupture of the heart)
Operative Suffix
These suffixes indicate a surgical procedure:
- -centesis: surgical puncture to remove fluid (e.g., amniocentesis — puncture of the amniotic sac)
Explanation
Medical suffixes are used to provide detailed information about the nature, origin, and type of medical conditions and procedures. Symptomatic suffixes help identify what a patient is feeling or experiencing. For example, both -algia and -dynia refer to pain, but might appear in different contexts depending on the root word. Understanding these helps in accurately describing symptoms such as arthralgia (joint pain) or myodynia (muscle pain).
Diagnostic suffixes allow medical professionals to label and define the exact condition or disease. A suffix like -itis indicates inflammation, which is crucial in identifying diseases such as tonsillitis or dermatitis. The suffix -emia indicates a condition of the blood, like leukemia, which involves white blood cells. Terms like -osis or -iasis describe abnormal conditions and help in categorizing chronic or infectious diseases.
Suffixes like -oma (tumor) and -rrhage (bursting) convey severity and urgency, affecting diagnosis and treatment plans. The suffix -rrhexis (rupture) suggests structural failure in tissues or organs, necessitating immediate attention.
Operative suffixes like -centesis describe the type of procedure performed. For instance, thoracentesis involves removing fluid from the chest cavity, which aids in treating pleural effusion.
Knowing these suffixes improves communication between healthcare providers and helps patients understand their conditions. They form the building blocks of medical terminology, supporting clear and precise diagnosis, documentation, and treatment across various specialties.
