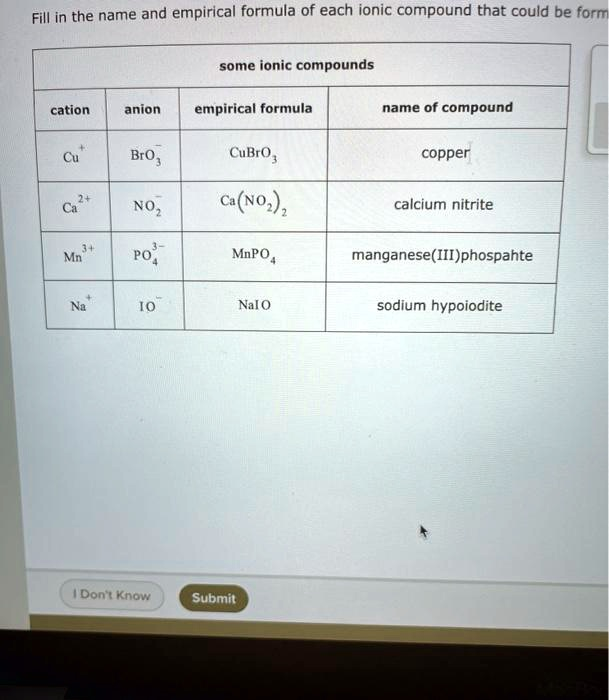
Fill in the name and empirical formula of each ionic compound that could be formed. cation anion empirical formula name of compound BrO CuBrO copper NOz calcium nitrite Mn Po MnPO manganese(III) phosphate Nal0 sodium hypoiodite Don't Know (NO3)1
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Let’s complete the table with the correct empirical formulas and compound names:
| Cation | Anion | Empirical Formula | Name of Compound |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cu²⁺ | BrO₃⁻ | Cu(BrO₃)₂ | copper(II) bromate |
| Ca²⁺ | NO₂⁻ | Ca(NO₂)₂ | calcium nitrite |
| Mn³⁺ | PO₄³⁻ | MnPO₄ | manganese(III) phosphate |
| Na⁺ | IO⁻ | NaIO | sodium hypoiodite |
| NO₃⁻ | — | — | nitrate (polyatomic anion) |
Explanation
Ionic compounds form when a metal cation combines with a nonmetal or polyatomic anion. The resulting formula is neutral in charge. The name reflects the metal ion’s oxidation state when it can have more than one.
Copper(II) bromate (Cu(BrO₃)₂): Copper forms a +2 ion. The bromate ion has a -1 charge. To neutralize the +2 charge on copper, two bromate ions are needed, forming Cu(BrO₃)₂. The roman numeral II indicates the +2 oxidation state.
Calcium nitrite (Ca(NO₂)₂): Calcium forms a +2 cation and nitrite is a -1 polyatomic anion. Balancing the charges requires two nitrite ions for every calcium ion.
Manganese(III) phosphate (MnPO₄): Manganese in the +3 state pairs with phosphate, which has a -3 charge. Since the charges are equal and opposite, they form a one-to-one combination.
Sodium hypoiodite (NaIO): Sodium is a +1 cation and hypoiodite is a -1 anion. Their charges balance one-to-one, forming NaIO.
Nitrate (NO₃⁻): This is an anion, not a compound. It would form compounds such as KNO₃ with potassium, or AgNO₃ with silver. Since no cation is listed alongside it, we cannot build a full compound.
