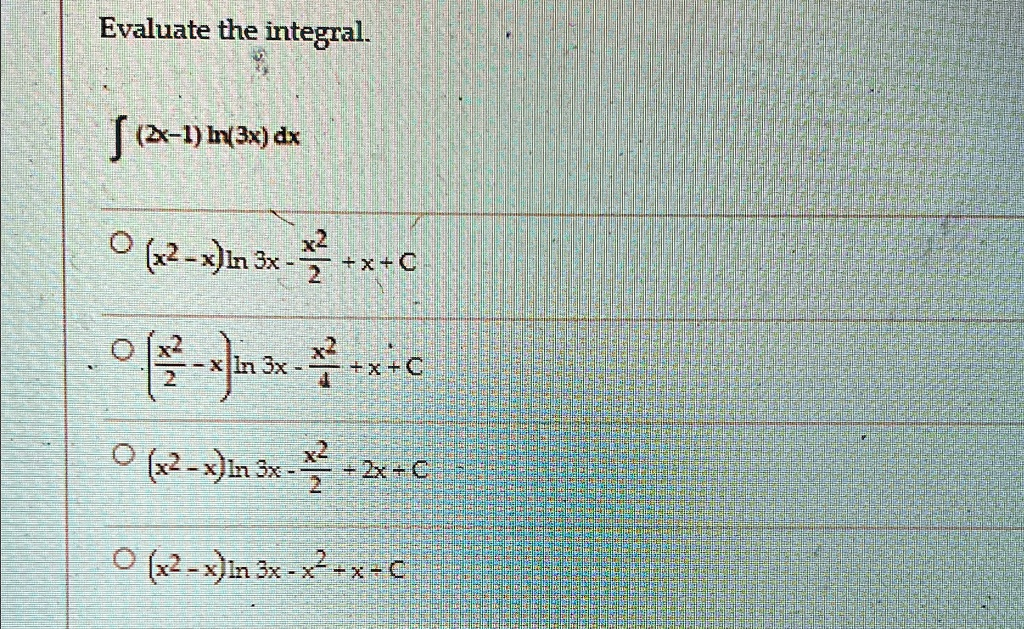
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
We are given the integral:∫(2x−1)ln(3x) dx\int (2x – 1)\ln(3x)\, dx∫(2x−1)ln(3x)dx
This integral involves a product of functions, so we apply integration by parts:
Step 1: Identify parts
Let:
- u=ln(3x)u = \ln(3x)u=ln(3x) so that du=1xdxdu = \frac{1}{x} dxdu=x1dx
- dv=(2x−1)dxdv = (2x – 1) dxdv=(2x−1)dx so that v=x2−xv = x^2 – xv=x2−x
Step 2: Apply the integration by parts formula
∫u dv=uv−∫v du\int u\, dv = uv – \int v\, du∫udv=uv−∫vdu
Substitute in:∫(2x−1)ln(3x) dx=(x2−x)ln(3x)−∫(x2−x)⋅1xdx\int (2x – 1)\ln(3x)\, dx = (x^2 – x)\ln(3x) – \int (x^2 – x) \cdot \frac{1}{x} dx∫(2x−1)ln(3x)dx=(x2−x)ln(3x)−∫(x2−x)⋅x1dx
Simplify the second integral:∫(x2−x)⋅1xdx=∫(x−1)dx=x22−x\int (x^2 – x) \cdot \frac{1}{x} dx = \int (x – 1) dx = \frac{x^2}{2} – x∫(x2−x)⋅x1dx=∫(x−1)dx=2×2−x
Step 3: Combine results
∫(2x−1)ln(3x) dx=(x2−x)ln(3x)−(x22−x)+C\int (2x – 1)\ln(3x)\, dx = (x^2 – x)\ln(3x) – \left( \frac{x^2}{2} – x \right) + C∫(2x−1)ln(3x)dx=(x2−x)ln(3x)−(2×2−x)+C=(x2−x)ln(3x)−x22+x+C= (x^2 – x)\ln(3x) – \frac{x^2}{2} + x + C=(x2−x)ln(3x)−2×2+x+C
Final Answer:
(x2−x)ln3x−x22+x+C\boxed{(x^2 – x)\ln 3x – \frac{x^2}{2} + x + C}(x2−x)ln3x−2×2+x+C
Correct multiple choice:
This matches the first choice in the image.Answer: First option\boxed{\text{Answer: } \text{First option}}Answer: First option
Explanation
To evaluate the integral ∫(2x−1)ln(3x) dx\int (2x – 1)\ln(3x)\, dx∫(2x−1)ln(3x)dx, we apply the technique of integration by parts. Integration by parts is used when the integrand is a product of two functions, and the formula is:∫u dv=uv−∫v du\int u\, dv = uv – \int v\, du∫udv=uv−∫vdu
We assign u=ln(3x)u = \ln(3x)u=ln(3x), which simplifies upon differentiation. Its derivative is du=1xdxdu = \frac{1}{x} dxdu=x1dx. The remaining part, dv=(2x−1)dxdv = (2x – 1)dxdv=(2x−1)dx, integrates to v=x2−xv = x^2 – xv=x2−x since the integral of 2x2x2x is x2x^2×2, and the integral of −1-1−1 is −x-x−x.
Using the integration by parts formula, we compute uv=(x2−x)ln(3x)uv = (x^2 – x)\ln(3x)uv=(x2−x)ln(3x), and then subtract the integral of v⋅duv \cdot duv⋅du, which becomes ∫(x2−x)⋅1xdx=∫(x−1)dx\int (x^2 – x)\cdot \frac{1}{x} dx = \int (x – 1) dx∫(x2−x)⋅x1dx=∫(x−1)dx. This simplifies to x22−x\frac{x^2}{2} – x2x2−x. Finally, putting everything together, we get:(x2−x)ln(3x)−(x22−x)+C(x^2 – x)\ln(3x) – \left( \frac{x^2}{2} – x \right) + C(x2−x)ln(3x)−(2×2−x)+C
This simplifies to the final answer:(x2−x)ln(3x)−x22+x+C(x^2 – x)\ln(3x) – \frac{x^2}{2} + x + C(x2−x)ln(3x)−2×2+x+C
Among the provided choices, this exactly matches the first option in the list.
