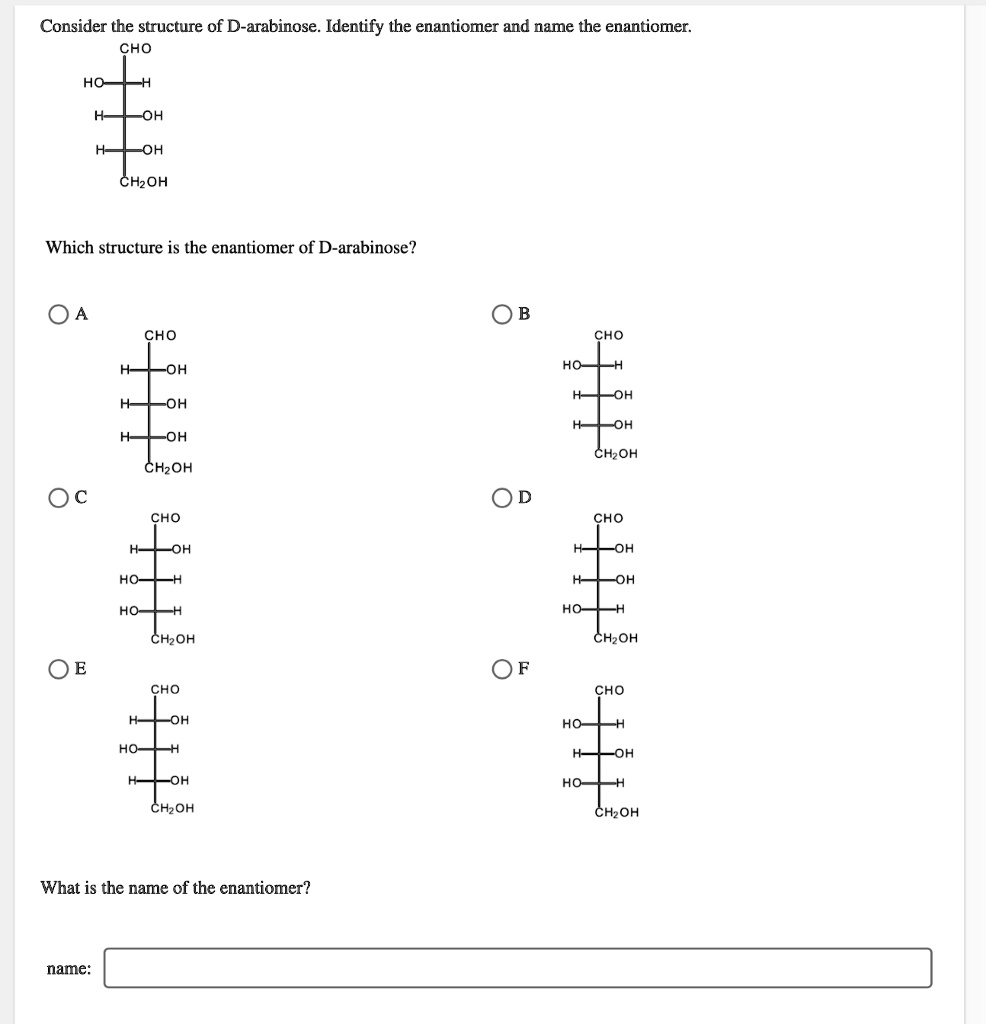
Consider the structure of D-arabinose. Identify the enantiomer and name the enantiomer: CHO HO OH OH CH2OH Which structure is the enantiomer of D-arabinose? A CHO CHO OH HO OH OH OH CH2OH CH2OH CHO CHO OH OH OH OH HO- OH HO HO CH2OH CH2OH OF CHO CHO OH HO HO OH OH HO CH2OH CH2OH What is the name of the enantiomer? name:
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
To identify the enantiomer of D-arabinose, we need to first understand the concept of enantiomers. Enantiomers are pairs of molecules that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. D-arabinose, as shown in the structure, has a specific configuration at each chiral center, and its enantiomer will differ in the configuration of these centers.
Upon analyzing the structures in the image and comparing them to D-arabinose, the enantiomer would be the one that has the opposite configuration at all of the chiral centers.
Enantiomer Identification:
- D-arabinose has the following configuration (from top to bottom):
- The hydroxyl group on the second carbon (C2) is on the right (as per the Fischer projection).
- The hydroxyl group on the third carbon (C3) is on the left.
- The hydroxyl group on the fourth carbon (C4) is on the right.
For the enantiomer of D-arabinose, the configurations at each of these centers should be reversed, meaning the hydroxyl groups will be flipped at each chiral center.
Name of the Enantiomer:
The enantiomer of D-arabinose is L-arabinose, as it is the mirror image of D-arabinose. The L and D notation refers to the configuration of the molecule relative to D- and L-glyceraldehyde, which is the reference compound for these terms. Specifically, L-arabinose has the same configuration at each chiral center as D-arabinose but with opposite stereochemistry.
Correct Answer:
The enantiomer of D-arabinose is L-arabinose, and the corresponding structure is the one where the hydroxyl groups are reversed at every chiral center.
