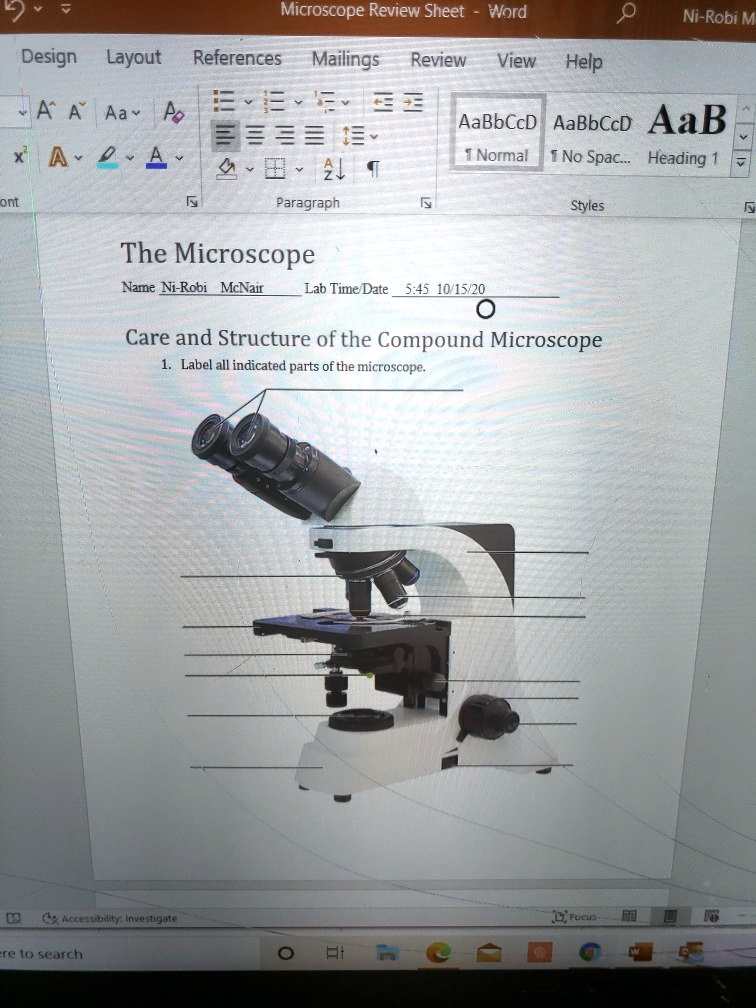
The Microscope Name Ni-Robi McNair Lab Time/Date 5:45 10/15/20 Care and Structure of the Compound Microscope 1. Label all indicated parts of the microscope.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Based on the image of the compound microscope provided, here are the correct labels for the indicated parts of the microscope (from top to bottom):
- Ocular Lens (Eyepiece) – The part you look through. It usually contains a 10x or 15x magnifying lens.
- Body Tube – Connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses.
- Revolving Nosepiece (Turret) – Holds multiple objective lenses and rotates to change magnification.
- Objective Lenses – Typically includes low (4x), medium (10x), high (40x), and sometimes oil immersion (100x) powers.
- Stage Clips – Hold the slide in place on the stage.
- Stage – The flat platform where the slide is placed for observation.
- Diaphragm – Controls the amount of light that reaches the specimen.
- Light Source – Illuminates the specimen, located beneath the stage.
- Arm – Supports the tube and connects it to the base; used to carry the microscope.
- Coarse Adjustment Knob – Moves the stage up and down for general focusing.
- Fine Adjustment Knob – Sharpens the focus of the image after using the coarse adjustment.
- Base – The bottom part that supports the microscope and houses the light source.
Explanation
A compound microscope is an essential tool in biology for viewing small specimens that cannot be seen with the naked eye. It uses a system of lenses to magnify the image of the specimen. Understanding the parts of the microscope is vital for proper use and accurate observation.
At the top, the ocular lens or eyepiece is where the viewer places their eye. This lens usually magnifies the image 10 or 15 times. Connected to it is the body tube, which ensures the correct alignment of the optical components.
The revolving nosepiece holds the objective lenses and allows for quick switching between different magnifications. The objective lenses are the most powerful lenses and come in varying powers. Together with the ocular lens, they determine the total magnification.
The stage is the flat surface where slides are placed. Stage clips help hold the slide in place during viewing. Beneath the stage is the diaphragm, which adjusts light intensity and contrast. The light source, located at the microscope’s base, illuminates the specimen from below.
The arm connects the upper parts of the microscope to the base and is used to carry the microscope. The coarse adjustment knob is used for large focusing movements, especially under low power. The fine adjustment knob makes smaller, more precise focus changes, especially under high power.
The base provides stability and support. Understanding these components ensures the microscope is used correctly, which is crucial for viewing specimens clearly and avoiding damage to the instrument.
