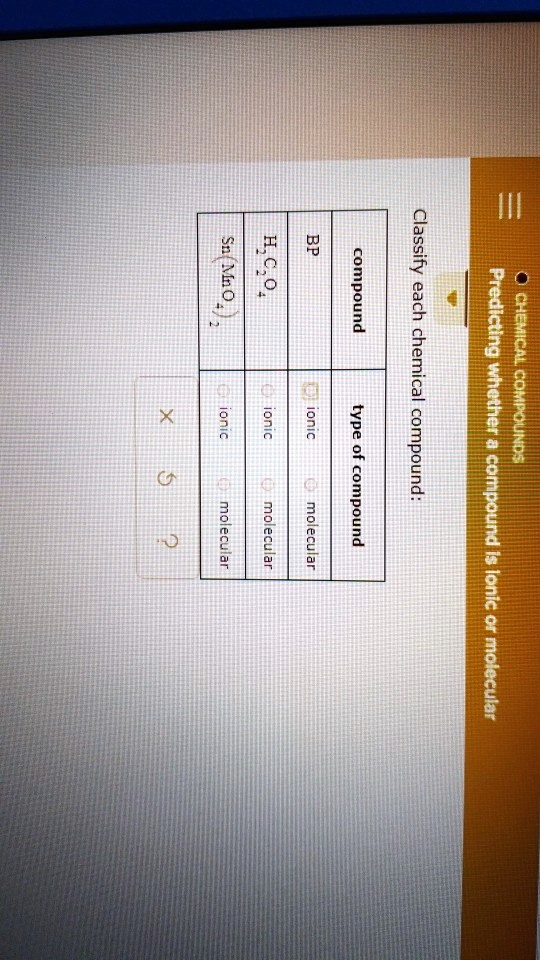
BP Classify 951 compounds each in chemical type 1 Ionic, Ionic, Ionic, 1 compound, compound, compound, molecular, molecular 2 Ionic 8 molecular.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Based on the principles of chemical bonding, here are the correct classifications for each compound:
- BP: Molecular
- H₂C₂O₄: Molecular
- Sn(MnO₄)₂: Ionic
Explanation
To determine if a compound is ionic or molecular, we look at the types of elements it contains. The general rule is that ionic compounds form between a metal and a nonmetal, while molecular (covalent) compounds form between two or more nonmetals.
BP (Boron Phosphide): This compound is formed from Boron (B) and Phosphorus (P). Boron is a metalloid, and Phosphorus is a nonmetal. Both elements are located on the right side of the periodic table and have relatively similar electronegativities. When elements with a small difference in electronegativity bond, they tend to share electrons, forming a covalent bond. Because the bond between boron and phosphorus is covalent, BP is classified as a molecular compound.
H₂C₂O₄ (Oxalic Acid): This compound consists of Hydrogen (H), Carbon (C), and Oxygen (O). All three of these elements are nonmetals. Bonds formed between nonmetal atoms are covalent, where electrons are shared. Since H₂C₂O₄ is composed entirely of nonmetals sharing electrons, it is a molecular compound. Acids are a specific class of molecular compounds.
Sn(MnO₄)₂ (Tin(II) Permanganate): This compound contains Tin (Sn) and the permanganate group (MnO₄). Tin is a metal, which typically forms a positive ion (cation) in chemical compounds. The permanganate group is a polyatomic anion, meaning it is a group of covalently bonded atoms (Manganese and Oxygen) that together have a negative charge (MnO₄⁻). The bond between a metal cation (Sn²⁺) and a polyatomic anion (MnO₄⁻) is due to electrostatic attraction. This type of bond is ionic. Therefore, Sn(MnO₄)₂ is an ionic compound.
