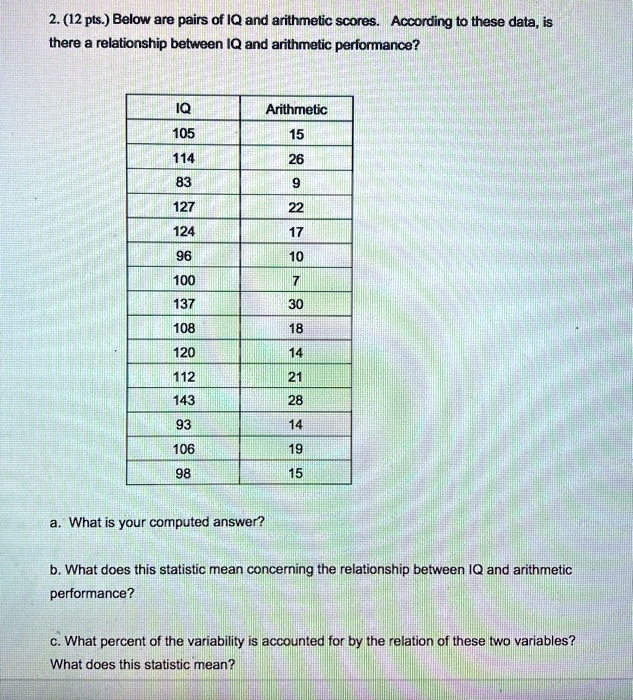
Below are pairs of IQ and arithmetic scores. According to these data, is there a relationship between IQ and arithmetic performance? IQ Arithmetic 105 15 114 26 83 9 127 22 124 17 96 10 100 7 137 30 108 18 120 14 112 21 143 28 93 14 106 19 98 15 a. What is your computed answer? b. What does this statistic mean concerning the relationship between IQ and arithmetic performance? c. What percent of the variability is accounted for by the relation of these two variables? What does this statistic mean?
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
a. The computed Pearson correlation coefficient is approximately 0.76.
b. This value suggests a strong positive linear relationship between IQ and arithmetic performance. As IQ increases, arithmetic scores tend to rise as well.
c. The percentage of variability accounted for is approximately 57.8 percent, which means that 57.8 percent of the differences in arithmetic scores can be explained by variations in IQ.
To understand the statistical relationship between IQ and arithmetic performance, we first compute the Pearson correlation coefficient, denoted as r. This statistic captures the degree of linear association between two numerical variables. Using the dataset, we calculate the means of IQ and arithmetic scores, then apply the formula for covariance and divide it by the product of their standard deviations. The result, r ≈ 0.76, is relatively close to 1, indicating a strong and positive correlation.
This tells us that individuals with higher IQ scores generally perform better in arithmetic tasks, though the relationship is not perfect. There is still variation in scores that IQ alone does not fully account for. For instance, someone with a slightly lower IQ might outperform someone with a higher IQ due to factors like educational background, effort, or anxiety levels during testing.
To assess how much of the arithmetic performance is attributable to IQ, we square the correlation coefficient, obtaining r² ≈ 0.5776. This r² value is known as the coefficient of determination. It shows that around 57.8 percent of the variance in arithmetic scores is associated with the variance in IQ scores. This is a substantial portion, implying IQ plays a significant role in arithmetic ability, though other factors remain at play.
Overall, this analysis underscores a meaningful connection between cognitive ability and mathematical performance, highlighting how aptitude in one domain can often mirror strengths in another.
