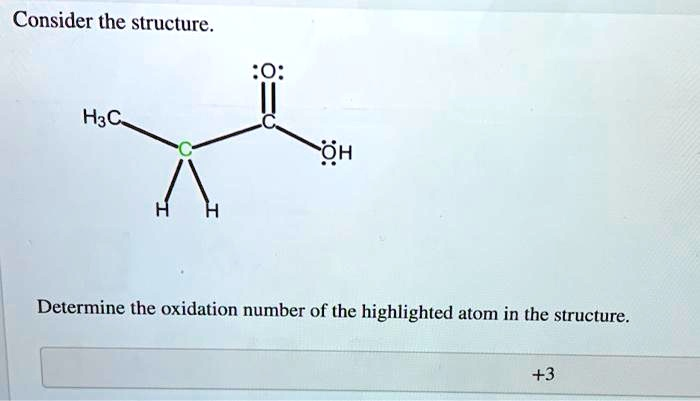
Consider the structure. H3C OH Determine the oxidation number of the highlighted atom in the structure. +3
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
To determine the oxidation number of the highlighted atom, we need to analyze the bonds connected to it and assign the bonding electrons based on electronegativity.
- Identify the highlighted atom and its bonds: The highlighted atom is the central carbon atom in the propanoic acid molecule. This carbon is part of a methylene group (-CH2-). It is bonded to:
- One carbon atom from the methyl group (H3C-).
- One carbon atom from the carboxyl group (-COOH).
- Two hydrogen atoms (-H).
- Apply electronegativity rules: The general order of electronegativity for the atoms involved is Oxygen > Carbon > Hydrogen.
- When two atoms in a bond have the same electronegativity (like a C-C bond), the bonding electrons are shared equally, and the bond does not contribute to the oxidation number of either atom.
- When two atoms have different electronegativity (like a C-H bond), the more electronegative atom is assigned all the bonding electrons.
- Calculate the contribution from each bond to the highlighted carbon’s oxidation number:
- C-C bond (with the methyl carbon): The atoms are the same, so the contribution is 0.
- C-C bond (with the carboxyl carbon): The atoms are the same, so the contribution is 0.
- C-H bond: Carbon is more electronegative than hydrogen. The carbon atom “takes” the electron from hydrogen, giving the carbon a charge of -1 from this bond.
- Another C-H bond: Similarly, this bond contributes -1 to the carbon’s oxidation number.
- Sum the contributions: To find the total oxidation number of the highlighted carbon, we add up the contributions from all its bonds:
Oxidation Number = (0) + (0) + (-1) + (-1) = -2
Therefore, the oxidation number of the highlighted carbon atom is -2.
(Note: The number “+3” visible at the bottom of the image is the oxidation number for the other carbon atom, the one in the carboxyl group (-COOH), not the highlighted one.)
