40 cm 20 cm 200 g 100 g What is the clockwise torque about the support point in the system shown above? What is the counterclockwise torque about the support point in the system shown above? Is the system shown above in equilibrium? How do you know?
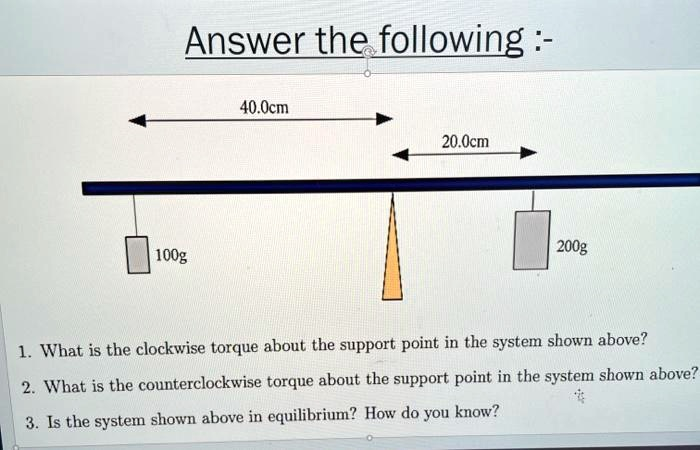
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Here are the answers to the questions based on the provided image.
1. What is the clockwise torque about the support point in the system shown above?
The clockwise torque is 4000 g·cm.
2. What is the counterclockwise torque about the support point in the system shown above?
The counterclockwise torque is 4000 g·cm.
3. Is the system shown above in equilibrium? How do you know?
Yes, the system is in equilibrium. This is because the clockwise torque is equal to the counterclockwise torque.
Explanation
To understand this system, we need to analyze the concept of torque. Torque is a measure of the turning force that an object applies around a pivot point, which in this case is the triangular support or fulcrum. It is calculated by multiplying the force applied by the perpendicular distance from the pivot point. The formula is:
Torque = Force × Distance
In this problem, the force is the weight of the masses. While force is technically mass times the acceleration due to gravity (g), we can use the mass values directly (in grams) and the distance (in centimeters) for comparison, as the value of g would be the same for both sides and would cancel out.
1. Clockwise Torque Calculation
The clockwise torque is created by the mass on the right side of the fulcrum, as it would cause the lever to rotate in a clockwise direction.
- Mass = 200 g
- Distance from fulcrum = 20.0 cm
Clockwise Torque = 200 g × 20.0 cm = 4000 g·cm
2. Counterclockwise Torque Calculation
The counterclockwise torque is created by the mass on the left side of the fulcrum, as it would cause the lever to rotate in a counterclockwise direction.
- Mass = 100 g
- Distance from fulcrum = 40.0 cm
Counterclockwise Torque = 100 g × 40.0 cm = 4000 g·cm
3. Determining Equilibrium
A system is in rotational equilibrium when it is not rotating. This occurs when the net torque on the system is zero. According to the Principle of Moments, for an object to be balanced, the sum of the clockwise torques must be exactly equal to the sum of the counterclockwise torques.
By comparing the two calculated values:
- Clockwise Torque = 4000 g·cm
- Counterclockwise Torque = 4000 g·cm
Since the clockwise and counterclockwise torques are equal, they cancel each other out completely. This means there is no net turning force acting on the lever. Therefore, the lever will remain balanced and stationary, proving the system is in equilibrium.
