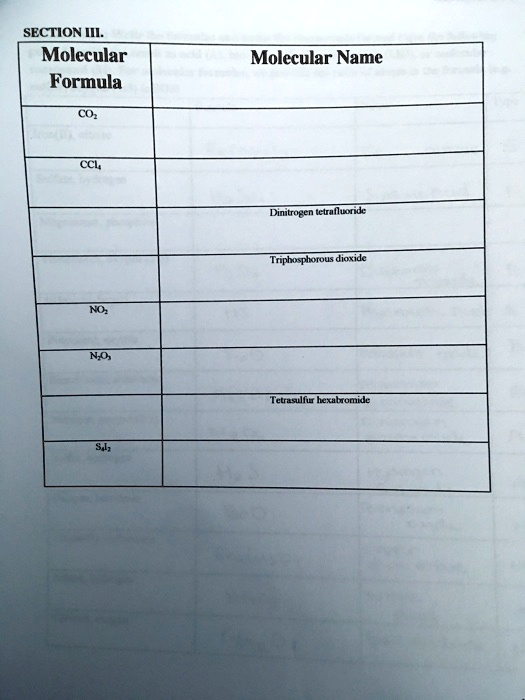
Molecular Name Molecular Formula CO? CCL? NO? N?O? S?l? Dinitrogen tetrafluoride Triphosphorous dioxide Tetrasulfur hexabromide
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Here’s the completed table with the correct molecular formulas and names filled in:
| Molecular Formula | Molecular Name |
|---|---|
| CO₂ | Carbon dioxide |
| CCl₄ | Carbon tetrachloride |
| N₂F₄ | Dinitrogen tetrafluoride |
| P₃O₂ | Triphosphorous dioxide |
| NO₂ | Nitrogen dioxide |
| N₂O₃ | Dinitrogen trioxide |
| S₄Br₆ | Tetrasulfur hexabromide |
🧪 Why These Answers? Let’s Break It Down:
This table is based on binary covalent compound naming rules, which typically involve two nonmetals. The first element keeps its name; the second gets a prefix and ends in -ide. Prefixes like mono-, di-, tri-, tetra-, etc., indicate the number of atoms.
- CO₂ → Carbon dioxide
Carbon is the first element, and since there are two oxygen atoms, we use “di-” for dioxide. - CCl₄ → Carbon tetrachloride
One carbon, four chlorine atoms. “Tetra-” for four. - N₂F₄ → Dinitrogen tetrafluoride
Two nitrogen atoms (di-), four fluorine atoms (tetra-). - P₃O₂ → Triphosphorous dioxide
Three phosphorus atoms (tri-), two oxygen atoms (di-). “Phosphorous” not “phosphorus” due to traditional naming conventions in covalent compounds. - NO₂ → Nitrogen dioxide
One nitrogen atom (no “mono” needed for the first element), two oxygen atoms (dioxide). - N₂O₃ → Dinitrogen trioxide
Two nitrogen atoms (di-), three oxygen atoms (tri-). - S₄Br₆ → Tetrasulfur hexabromide
Four sulfur atoms (tetra-), six bromine atoms (hexa-).
These names reflect molecular ratios directly from their subscripts. It’s like chemistry’s version of relationship status: complicated, but consistent 😂💥.
