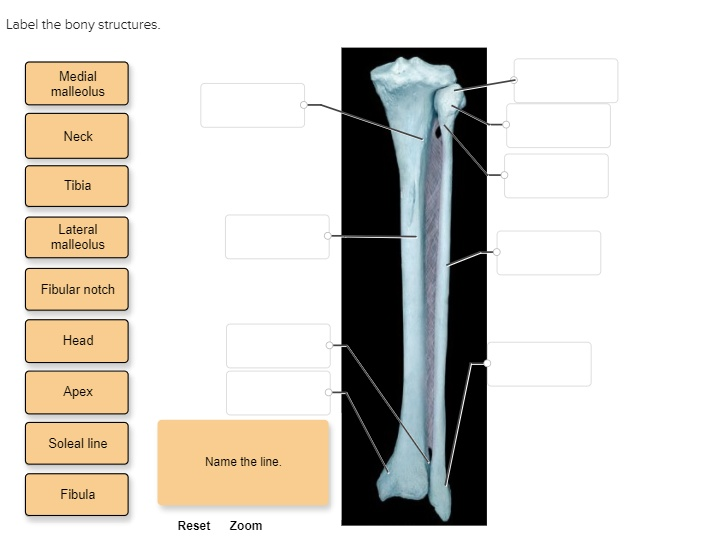
Label the bony structures. Medial malleolus Neck Tibia Lateral malleolus Fibular notch Head Apex Soleal line Name the line. Fibula Reset Zoom
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Based on the diagram of the tibia and fibula, here are the correct anatomical labels:
- Head – proximal end of the fibula, articulates with the tibia.
- Neck – just below the head of the fibula.
- Apex – pointed projection of the fibula near the head.
- Fibula – slender, lateral bone of the lower leg.
- Lateral malleolus – distal projection of the fibula on the outer ankle.
- Fibular notch – indentation on the tibia that articulates with the fibula.
- Tibia – larger, weight-bearing bone on the medial side of the leg.
- Soleal line – oblique ridge on the posterior surface of the tibia.
- Medial malleolus – distal projection of the tibia on the inner ankle.
- Name the line – this is the interosseous membrane, a fibrous sheet connecting the tibia and fibula.
Explanation:
The lower leg comprises two long bones, the tibia and the fibula. The tibia is thicker and positioned medially, bearing most of the body’s weight, while the fibula lies laterally and provides structural support and muscle attachment points.
At the proximal end of the fibula, the head articulates with the lateral condyle of the tibia, with the neck just inferior to it and the apex marking a pointed projection. The shaft of the fibula extends distally to the lateral malleolus, a critical structure in ankle stability.
The tibia features the soleal line on its posterior surface, which serves as the origin for the soleus muscle, contributing to plantarflexion during walking. Distally, the medial malleolus projects medially at the ankle, mirroring the fibula’s lateral malleolus.
The fibular notch is found on the distal tibia and forms part of the syndesmosis joint with the fibula. Spanning between the tibia and fibula is the interosseous membrane, a crucial connective structure that stabilizes the bones and allows for force transmission.
Understanding this anatomy is vital in fields like orthopedics and sports medicine, especially when diagnosing fractures, managing sprains, or planning surgical interventions.
