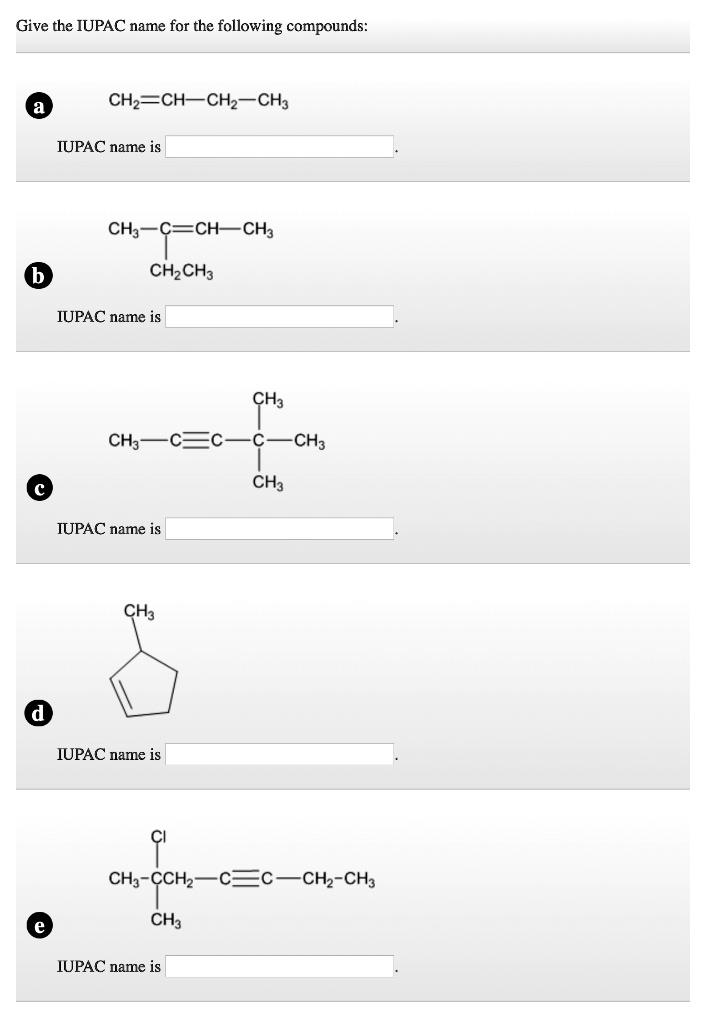
Give the IUPAC name for the following compounds: a CH2=CH-CH2-CH3 IUPAC name is CH3-C=CH-CH3 b CH2CH3 IUPAC name is d e CH3 CH3-C?C-C-CH3 CH3 IUPAC name is CH3 IUPAC name is CH3-CCH2-C?C-CH2-CH3 CH3 IUPAC name is
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Here are the correct IUPAC names for the compounds shown in the image:
a) CH₂=CH−CH₂−CH₃ → But-1-ene
b) The structure corresponds to a triple bond between C2 and C3 in a five-carbon chain with an ethyl substituent on C4: CH₃−C≡C−CH(CH₂CH₃)−CH₃ → 4-Ethylpent-2-yne
c) A four-carbon chain with a triple bond starting at C1 and two methyl groups on C3: CH₃−C≡C−C(CH₃)₂−CH₃ → 3,3-Dimethylbut-1-yne
d) Cyclopentane with one methyl substituent: → Methylcyclopentane
e) Six-carbon chain with a triple bond between C2 and C3, a chlorine and a methyl both on C4: CH₃−C(Cl)(CH₃)−C≡C−CH₂−CH₃ → 4-Chloro-4-methylhex-2-yne
Explanation
IUPAC naming provides a consistent method for identifying chemical compounds based on structure.
In compound (a), But-1-ene consists of a four-carbon chain (but-) with a double bond between C1 and C2. The double bond takes priority in numbering, so the location is specified as position 1.
In (b), we identify a five-carbon chain (pentane backbone) with a triple bond starting at C2, hence “pent-2-yne.” An ethyl group (CH₂CH₃) on C4 makes it 4-ethylpent-2-yne.
Compound (c) has a butyne skeleton. The parent chain is four carbons long with a triple bond beginning at C1, so “but-1-yne.” Two methyl groups are attached to C3, giving 3,3-dimethylbut-1-yne.
(d) features a cyclopentane ring (five carbons in a closed loop) with a methyl group substituent. Since the ring has only one substituent, there’s no need for numbering. The name becomes methylcyclopentane.
In (e), the base chain has six carbon atoms (hexane), and there is a triple bond between C2 and C3 (hence “hex-2-yne”). The central carbon (C4) bears both a chlorine atom and a methyl group, resulting in 4-chloro-4-methylhex-2-yne.
These names follow priority rules for selecting parent chains, functional groups, and substituent placement. The goal is to minimize locants for principal groups such as multiple bonds, while maintaining alphabetic order for substituents in the name.
